16. Decorator Pattern
Decorator Pattern
ND079 JPND C2 L03 A16 Decorator Pattern
The Decorator Pattern
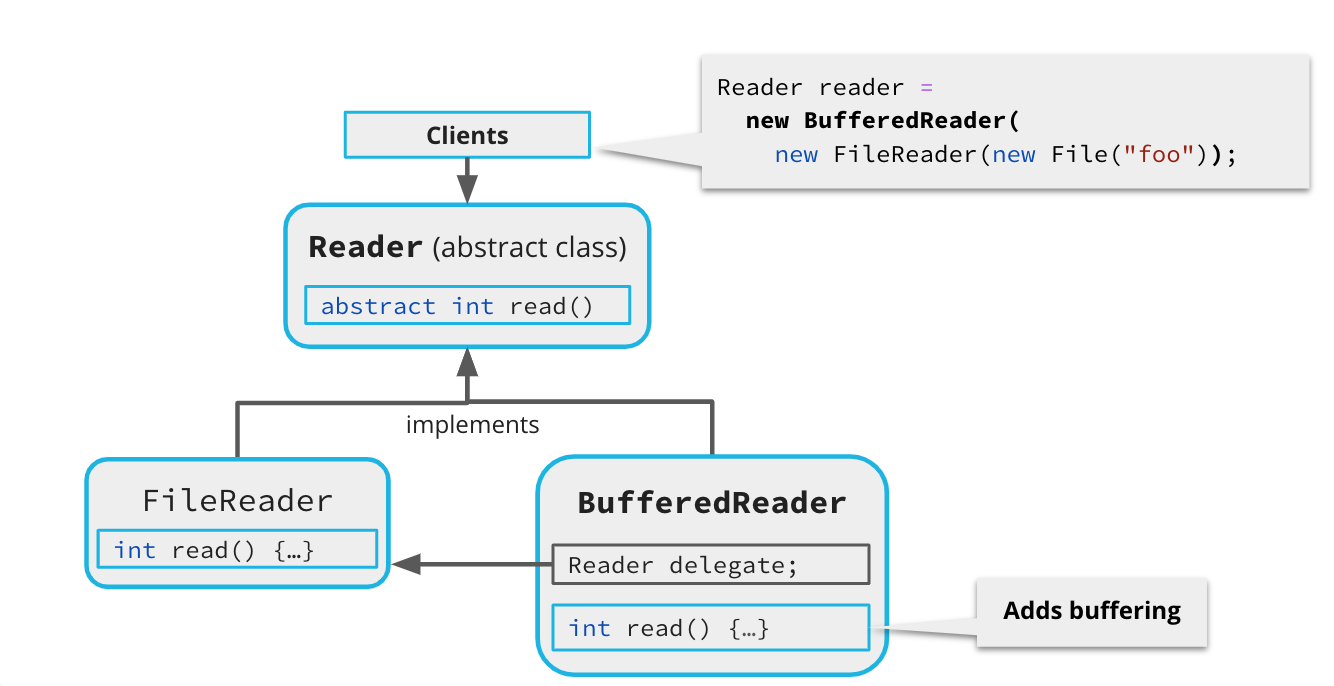
Java Implements BufferedReader Using the Decorator Pattern
SOLUTION:
Adds new functionality to an existing object dynamically by "wrapping" it. Favoring composition.Demo
ND079 JPND C2 L03 A17 Demo Decorator Pattern
Code from the Demo
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.Reader;
import java.util.Objects;
public final class CountReads {
public static final class CountingReader extends Reader {
private int count = 0;
private final Reader delegate;
CountingReader(Reader delegate) {
this.delegate = Objects.requireNonNull(delegate);
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
@Override
public int read(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) throws IOException {
count++;
return delegate.read(cbuf, off, len);
}
@Override
public void close() throws IOException {
delegate.close();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
try (FileReader reader = new FileReader(new File("randomtext.txt"))) {
CountingReader unbufferedReads = new CountingReader(reader);
CountingReader bufferedReads = new CountingReader(new BufferedReader(unbufferedReads));
char[] data = new char[100];
while (bufferedReads.read(data) != -1);
System.out.println("Calls to BufferedReader.read(): " + bufferedReads.getCount());
System.out.println("Calls to FileReader.read(): " + unbufferedReads.getCount());
}
}
}In this demo, we wrote a decorator that counted the number of reads to a Reader. The decorator proved that the BufferedReader reduced the number of reads from disk by about 90%. Pretty good!
** Adapter vs Decorator **
- These patterns both "wrap" another object, called the delegate.
- An Adapter returns a different interface than the delegate.
- A Decorator returns the same interface, but with added functionality or responsibilities.
- A Proxy is similar to a Decorator, but the proxy usually controls or manages access to the delegate.
SOLUTION:
Both these patterns "wrap" a delegate class instead of inheriting from it.QUIZ QUESTION::
Match each structural design pattern with its description.
ANSWER CHOICES:
|
Description |
Pattern |
|---|---|
Wraps an API, adding additional functionality. |
|
Transforms one API into a different API. |
|
Controls access to a delegate object. |
SOLUTION:
|
Description |
Pattern |
|---|---|
|
Transforms one API into a different API. |
|
|
Controls access to a delegate object. |
|
|
Wraps an API, adding additional functionality. |